December Releases: Rebecca, Not Becky & You Bury the Birds in My Pelvis
The last month of the year is generally thin on the ground for new books, but here are two December U.S. releases I reviewed early for Shelf Awareness. One is a fun and timely novel about race relations and the other an autobiographical poetry collection about asexuality and chronic illness. Below are excerpts with a link to the full text for one. Both: 
Rebecca, Not Becky by Christine Platt and Catherine Wigginton Greene
 Two women navigate the nuances of racism in their affluent Northern Virginia community. Rebecca Myland shed the nickname “Becky” when it became cultural shorthand for clueless white ladies. She desperately wants to do the right thing, including making the perfect home for her husband and daughters and being a model white ally, leading the school’s diversity committee and antiracist book club.
Two women navigate the nuances of racism in their affluent Northern Virginia community. Rebecca Myland shed the nickname “Becky” when it became cultural shorthand for clueless white ladies. She desperately wants to do the right thing, including making the perfect home for her husband and daughters and being a model white ally, leading the school’s diversity committee and antiracist book club.
De’Andrea Whitman reluctantly gave up her law career and Atlanta support system to move to Rolling Hills. It’s the best place for the family, given her husband Malik’s new job and the proximity to his mother’s top-notch dementia care facility. However, she is painfully aware that their daughter, Nina, may be the only Black student at the private school. De’Andrea’s therapist, Dr. Jones, challenges her to try to make one white friend.
The two protagonists have more in common than they realize. When the diversity committee’s controversial pet project of getting a statue of a Confederate general removed from the local park makes national news, the resulting ruckus threatens their fragile friendship. It’s a hugely enjoyable novel reminiscent of Terry McMillan and Curtis Sittenfeld that nonetheless takes a hard look at prejudice and performative allyship.
(And I love the title because my mother and one aunt always tried to call me Becky, but I hate that nickname!)
You Bury the Birds in My Pelvis by Kelly Weber
 The poet feels marked by “failure to want” and by recurring medical complaints—severe Crohn’s disease and menorrhagia, initially dismissed by a doctor as menstrual cramps. In “Blood Firsts,” she compares her first period with the later coming-of-age moment of realizing she was asexual. She describes herself as a teenage wallflower, aware of a same-sex pull but unsure what, if anything, to do about it. The series of lyrical attempted definitions in “Queerplatonic” show her in love with a female friend. Anatomy and nature supply the book’s interlocking metaphors. Animals appear frequently, but often as roadkill or taxidermied trophies. The structure varies, with prose paragraphs, columns, and text moving up the page. The rich stylistic palette (rhetorical questions, footnotes, second person, a call-and-response format) and sonic arsenal (alliteration, wordplay, anaphora) make for a courageous, unforgettable collection. (Forthcoming)
The poet feels marked by “failure to want” and by recurring medical complaints—severe Crohn’s disease and menorrhagia, initially dismissed by a doctor as menstrual cramps. In “Blood Firsts,” she compares her first period with the later coming-of-age moment of realizing she was asexual. She describes herself as a teenage wallflower, aware of a same-sex pull but unsure what, if anything, to do about it. The series of lyrical attempted definitions in “Queerplatonic” show her in love with a female friend. Anatomy and nature supply the book’s interlocking metaphors. Animals appear frequently, but often as roadkill or taxidermied trophies. The structure varies, with prose paragraphs, columns, and text moving up the page. The rich stylistic palette (rhetorical questions, footnotes, second person, a call-and-response format) and sonic arsenal (alliteration, wordplay, anaphora) make for a courageous, unforgettable collection. (Forthcoming)
20 Books of Summer, 11–12: Gillian Clarke Poetry and Ross Gay Essays
It might not look like I’ll finish the 20 Books of Summer challenge in time, but I’ve got it all planned out and should be reviewing the last few on the final day! My initial foodie idea has turned into a micro-theme that joins only about six of the titles in total. I’ve swapped in various other things along the way, such as a couple of poetry collections and novellas (note to self: always include at least a few very short books!), but the focus has been on getting through stuff from my own shelves, especially recent acquisitions and work by women.
Today I have an excellent poetry collection infused with the language of gardening and geology and reflecting on two crises of the early 2000s, and a book of mini-essays about noticing the small pleasures that make life worth living.
Making the Beds for the Dead by Gillian Clarke (2004)
 I look out for black-and-white Carcanet spines whenever I’m scanning the poetry section in a secondhand bookshop. Clarke’s was a new name for me (the National Poet of Wales from 2008 to 2016, she’s now 86) but the blurb attracted me and this ended up being exactly the sort of poetry I love: full of colours and nature imagery, profuse with alliteration and slant rhymes, relishing its specialist terminology, and taking on the serious subject matter of manmade disasters. Several medium-length sequences are devoted to gardening (“The Middleton Poems” and “Nine Green Gardens”) and geology (“The Stone Poems”); some earlier pieces are ekphrastic, or dedicated to particular poets.
I look out for black-and-white Carcanet spines whenever I’m scanning the poetry section in a secondhand bookshop. Clarke’s was a new name for me (the National Poet of Wales from 2008 to 2016, she’s now 86) but the blurb attracted me and this ended up being exactly the sort of poetry I love: full of colours and nature imagery, profuse with alliteration and slant rhymes, relishing its specialist terminology, and taking on the serious subject matter of manmade disasters. Several medium-length sequences are devoted to gardening (“The Middleton Poems” and “Nine Green Gardens”) and geology (“The Stone Poems”); some earlier pieces are ekphrastic, or dedicated to particular poets.
Clarke remembers the delight she took as a child in the unfamiliar vocabulary of the Bible, “a narrative of spells / in difficult columns on those moth-thin pages, / words to thrill the heart with a strange music.” The book teems with animals – though, alas, many of them are dead (as in “Adders” and “Taxidermy”). The title sequence, indeed is about the foot and mouth disease outbreak that decimated the UK livestock population in 2001. Farmers were forced to cull their flocks and news footage showed mountains of carcasses burning. She hovers over the catastrophe, imagining herself into the minds of family farmers, gossiping onlookers, and a traumatized vet. Just as one crisis was coming to an end, September 11 came – another unforgettable tragedy, commemorated with “The Fall.” A very affecting collection, all told. I’ll be sure to read more by Clarke. (Secondhand – Bridport Old Books, 2023) 
A favourite passage, from “The Yew Tunnel in Winter”:
Listen to sap rise, unstoppable flood,
for all the centuries as the tap-roots grew,
pumping through branches to the stirring bud
from deepest earth. In graveyards they say a yew
sends a root into the mouths of all the dead.
Here, sense all that power snowed in and still,
shut in the dream of winter and history
at the end of a muffled lane
The Book of Delights by Ross Gay (2019)
“Perhaps delight is like after the great cosmic finger has pointed at something, and that something … appears.”
Gay is better known as a poet, with several collections to his name, and teaches at Indiana University. This book project started as a challenge to self to write a daily essay about something that was good in his life, quickly and longhand. He started on his 42nd birthday (August 1) and continued for a full year; there are 102 micro-essays here, so he managed one every few days. They are about everything or nothing much, depending on how you look at it: an adored foodstuff or piece of music, a dream, a surprise encounter with a stranger, what was growing in his garden at the time, etc.
 One essay is titled “The Jenky,” about the crooked and makeshift. Gay watches the birds enjoying a dead tree in his (deliberately neglected) yard, and notes a sign reading “Caution: Bees on Bridge” and thereby making space for nature. A few of the more memorable incidents involve plane travel. One time he flies with a tomato seedling in his lap and finds that people treat him more kindly. He gets an unexpectedly enthusiastic response from a security guard when he mentions that he’s on his way to read poems and realizes later that, by some quirk of regional American accents, the man thought he’d said “reading palms.”
One essay is titled “The Jenky,” about the crooked and makeshift. Gay watches the birds enjoying a dead tree in his (deliberately neglected) yard, and notes a sign reading “Caution: Bees on Bridge” and thereby making space for nature. A few of the more memorable incidents involve plane travel. One time he flies with a tomato seedling in his lap and finds that people treat him more kindly. He gets an unexpectedly enthusiastic response from a security guard when he mentions that he’s on his way to read poems and realizes later that, by some quirk of regional American accents, the man thought he’d said “reading palms.”
Although I enjoyed the book more as I went along, something held me back from loving it. There weren’t enough sentiments that I recognized, and the loose, informal style wasn’t always for me. While you get glimpses into his upbringing and travels, I tend to prefer a memoir. It may also be that Gay and I are just different personalities. The delight he takes in other people’s oddities suggests he might be an extrovert; he truly enjoys being spoken to, or even touched (on the shoulder, for instance), by strangers, whereas I don’t particularly. Part of this is about minority group bonding for him: he writes of the “Negreeting” exchanged between Black people passing each other on a street. There were also a few too many mentions of him peeing into bottles or in his car.
So I liked this, but maybe not enough to try more by Gay, though I should probably see what his verse is like. I was glad to have read it, especially when I realized I can only think of about 20 books I’ve read by Black men. Ever. Yikes. (New – Christmas gift, 2022) 
September Releases: Gyasi, McKay, Sheldrake, Tremain, Woolfson
September is always a big month in the publishing world, but even more so this year because of all the titles delayed from the spring and summer – apparently 600 books were published in the first week of September in the UK alone.
Still, I only ended up with my usual, manageable five new releases (with a few more on the way from the library). I read a beautiful novel about addiction and religion in contemporary America, speculative fiction about communication with wildlife in mid-pandemic (!) Australia, everything you ever wanted to know about fungi, historical fiction about outsiders in England and Borneo, and a study of our broken relationship with other animals.
Two of these are from my most anticipated list for the second half of 2020. Four of the five can be linked by the tenet that humans are only one species among many others necessary to life on this Earth, and not in some way above and beyond.
Transcendent Kingdom by Yaa Gyasi
 This follow-up to Gyasi’s dazzling, centuries-spanning linked story collection, Homegoing, won’t be out in the UK until March 2021, but I couldn’t resist reading an e-copy of the American edition (Knopf) from Edelweiss. It’s altogether a more subdued and subtle book, but its treatment of themes of addiction, grief, racism and religion is so spot on that it packs a punch. Gifty is a PhD student at Stanford, researching pleasure and reward circuits in the mouse brain. She gets mice hooked on a sugary drink and then performs experiments to see if she can turn off their compulsion to keep pressing a lever for more. Sometimes when they press the lever they get an electric shock. Certain mice give up; others never will. Why?
This follow-up to Gyasi’s dazzling, centuries-spanning linked story collection, Homegoing, won’t be out in the UK until March 2021, but I couldn’t resist reading an e-copy of the American edition (Knopf) from Edelweiss. It’s altogether a more subdued and subtle book, but its treatment of themes of addiction, grief, racism and religion is so spot on that it packs a punch. Gifty is a PhD student at Stanford, researching pleasure and reward circuits in the mouse brain. She gets mice hooked on a sugary drink and then performs experiments to see if she can turn off their compulsion to keep pressing a lever for more. Sometimes when they press the lever they get an electric shock. Certain mice give up; others never will. Why?
People who know Gifty well assume she chose her field because of a personal tragedy. When she was 10, her 16-year-old brother, Nana, a high school basketball star in this Ghanaian-American family’s Alabama town, died of an opiate overdose. He’d gotten addicted to prescription drugs after a sports injury. At one level, Gifty acknowledges she is trying to atone for her brother’s death, but she won’t see it in those terms. An intensely private person, she shoulders almost impossible burdens of grief and responsibility for her mother, who has plunged into depression and, when she comes to live with Gifty, spends all her time in bed.
The most compelling aspect of the novel for me was Gifty’s attitude towards the religion of her childhood. Though they were the only black family at their Pentecostal church, she was a model believer, writing prayers in her journal, memorizing scriptures, and never doubting that everything happens for a reason. Nana’s death shattered it all. Though she now looks to science for answers, she misses the certainty she once had: that she was saved, that humans are special, that someone was looking out for her and her family, that it all mattered. I highlighted dozens of passages, but it’s possible the book won’t mean quite as much to readers for whom there’s no personal resonance. The complex mother–daughter relationship is an asset, and musings on love and risk are tenderly expressed. I wanted a more climactic conclusion to take this into 5-star territory, but I’ve still added it to my Best of 2020 shelf.
Favorite lines:
the species Homo sapiens, the most complex animal, [is] the only animal who believed he had transcended his Kingdom, as one of my high school biology teachers used to say.
At times, my life now feels so at odds with the religious teachings of my childhood that I wonder what the little girl I once was would think of the woman I’ve become … I am looking for new names for old feelings. My soul is still my soul, even if I rarely call it that.
the more I do this work the more I believe in a kind of holiness in our connection to everything on Earth. Holy is the mouse.
My rating: 
I read an advanced e-copy via Edelweiss.
The Animals in That Country by Laura Jean McKay
 McKay has a PhD in literary animal studies and serves as an animal expert and presenter on Australia’s ABC radio show Animal Sound Safari. Pair her academic background with the fact that this shares a title with a Margaret Atwood poetry collection and you’ll have some idea of what to expect here: mysterious but mostly believable speculative fiction that hinges on human communication with animals.
McKay has a PhD in literary animal studies and serves as an animal expert and presenter on Australia’s ABC radio show Animal Sound Safari. Pair her academic background with the fact that this shares a title with a Margaret Atwood poetry collection and you’ll have some idea of what to expect here: mysterious but mostly believable speculative fiction that hinges on human communication with animals.
Jean Bennett isn’t your average grandma: a wise-cracking alcoholic, she drives the tourist train through the Australian wildlife park her daughter-in-law manages but wishes she could be a fully fledged ranger. Her ex-husband, Graham, left her and went down south, and eventually their only son Lee did the same. Now all Jean has left is Kim, her six-year-old granddaughter. Jean entertains Kim by imagining voices for the park’s animals. This no longer seems like a game, though, when news filters through of the “zooflu,” which has hit epidemic levels and has as a main symptom the ability to understand what animals say.
When Kim is kidnapped, Jean steals a camper van and takes Sue the dingo along to help her find her granddaughter. “There’s a new normal now,” a bus driver tells her. “And around here, not wearing a mask means you’ve gone animal. I’d put on my protective if I was you. Put that mutt in a cage.” It was uncanny reading this in the midst of a pandemic, but the specifics of McKay’s novel are hard to grasp. The animal language isn’t audible, necessarily, but a combination of smells, noises and body language. For a long time, they seem like pure nonsense, but gradually they resemble a sort of rough poetry. Here’s one example from Sue:
My front end
takes the food
quality.
Muzzle
for the Queen
(Yesterday).
(Sue usually calls Jean “Queen” or “Mother,” showing that she respects her authority, and “Yesterday” is frequently used to suggest a primitive sense of the past or of an older person.)
As entertaining a protagonist as Jean is, I lost interest in her road trip. If you focus on the journey into the wilderness and don’t mind a sudden ending, you may find this a worthwhile heir to Hollow Kingdom by Kira Jane Buxton and The Road by Cormac McCarthy.
My rating: 
I read a proof copy for a Nudge review, but it’s never shown up on their website.
Entangled Life: How Fungi Make Our Worlds, Change Our Minds, and Shape Our Futures by Merlin Sheldrake
 I first heard about Sheldrake through Robert Macfarlane’s Underland. He struck me as a mad genius – an impression that was only strengthened by reading his detailed, enthusiastic book about fungi. Sheldrake researches fungal life in the tropical forests of Panama, accompanies truffle hunters in Italy, takes part in a clinical study on the effects of LSD (derived from a fungus), observes lichens off the coast of British Columbia, and attends a conference in Oregon on Radical Mycology. But more than a travel memoir, this is a work of science – there are over 100 pages devoted to notes, bibliography and index.
I first heard about Sheldrake through Robert Macfarlane’s Underland. He struck me as a mad genius – an impression that was only strengthened by reading his detailed, enthusiastic book about fungi. Sheldrake researches fungal life in the tropical forests of Panama, accompanies truffle hunters in Italy, takes part in a clinical study on the effects of LSD (derived from a fungus), observes lichens off the coast of British Columbia, and attends a conference in Oregon on Radical Mycology. But more than a travel memoir, this is a work of science – there are over 100 pages devoted to notes, bibliography and index.
Basic information you’ll soon learn: mushrooms are only the fruiting bodies of fungi; under the ground is the material bulk, the mycelium, a sprawling network of hyphae. In what’s sometimes called the “Wood Wide Web,” fungal networks link the trees in a forest, and join up with plants, such as in lichens. “I feel a … sense of vertigo when I think about the complexity of mycorrhizal relationships – kilometers of entangled life – jostling beneath my feet,” Sheldrake confesses. He gives examples of fungi navigating and solving problems – what of our concept of intelligence if a creature without a brain can do such things?
Fungi are very adaptable to extreme conditions. Research is underway to grow edible mushrooms on some of our most troublesome waste, such as used diapers (nappies) and cigarette butts. And, of course, for millennia we’ve relied on certain fungi – yeasts – to create products like bread and beer. Sheldrake is a very hands-on writer: When he wants to know something, he does it, whether that’s scrumping Isaac Newton’s apples in Cambridge and fermenting the juice into cider at home or growing mushrooms on a copy of this very book.
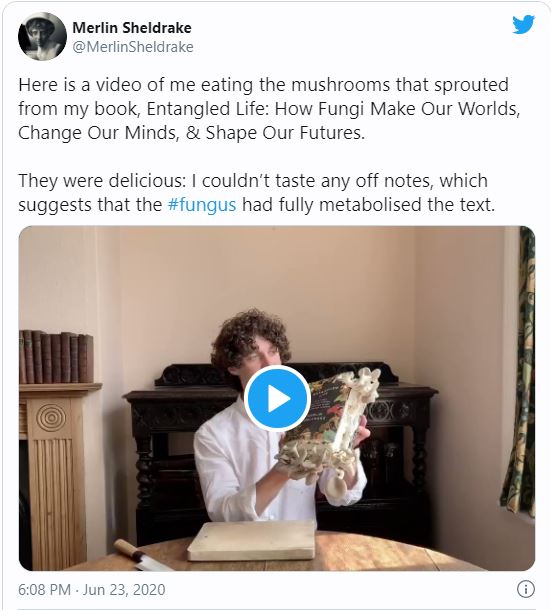
During the month I was reading this, I felt like I kept coming across references to fungi. (I even had a patch of ringworm!)

It’s a perspective-altering text, but one that requires solid concentration. I’ll confess that at times it went over my head and I wished for a glossary and diagrams. A greater than average interest in biology and/or botany would thus be a boon to a potential reader. But if you can keep up, the book will elicit many a cry of “wow!” and “what?!” I kept launching “did you know?” questions at my husband, especially about the zombie fungi that parasitize insects. What a strange and wonderful world.
Favorite lines: “Paying more attention to animals than plants contributes to humans’ plant-blindness. Paying more attention to plants than fungi makes us fungus-blind.”
My rating: 
My thanks to Bodley Head for the free copy for review.
Islands of Mercy by Rose Tremain
 I read this back in June to prepare for writing a profile of Tremain for a forthcoming issue of Bookmarks magazine. Here’s the summary I wrote: “In Bath, England in 1865, 24-year-old nurse Jane Adeane is nicknamed ‘The Angel of the Baths’ for her healing touch. If she marries Dr. Valentine Ross, a colleague of her surgeon father, she can earn respectability – but will have to hide her love for Julietta, a married woman. Meanwhile, Dr. Ross’s brother, Edmund, a naturalist following in the footsteps of Alfred Russel Wallace, has journeyed to Borneo. Ill with malaria, he is taken in by British eccentric Sir Ralph Savage, a lover of native men and benevolent local rajah who funds infrastructure projects like a paved road and a hospital. Exiled or inwardly tortured for loving the wrong people, Tremain’s characters search for moments of wonder and comfort – whether those come in a primitive hut in the Malay Archipelago or in a cozy tearoom in Bath.”
I read this back in June to prepare for writing a profile of Tremain for a forthcoming issue of Bookmarks magazine. Here’s the summary I wrote: “In Bath, England in 1865, 24-year-old nurse Jane Adeane is nicknamed ‘The Angel of the Baths’ for her healing touch. If she marries Dr. Valentine Ross, a colleague of her surgeon father, she can earn respectability – but will have to hide her love for Julietta, a married woman. Meanwhile, Dr. Ross’s brother, Edmund, a naturalist following in the footsteps of Alfred Russel Wallace, has journeyed to Borneo. Ill with malaria, he is taken in by British eccentric Sir Ralph Savage, a lover of native men and benevolent local rajah who funds infrastructure projects like a paved road and a hospital. Exiled or inwardly tortured for loving the wrong people, Tremain’s characters search for moments of wonder and comfort – whether those come in a primitive hut in the Malay Archipelago or in a cozy tearoom in Bath.”
It’s a slightly odd title, but tells you a lot about what Tremain is doing in this 14th novel. Often at the mercy of forces internal and external, her outcast characters look for places where they can find rest and refuge after a time of suffering. Will they, in turn, extend mercy? The split perspective and the focus on people who have to hide their sexuality are most similar to Sacred Country. The Victorian tip of the hat is mostly directed, I think, to George Eliot; of recent work, I was reminded of The Doll Factory and The Essex Serpent. I especially liked Jane’s painter aunt, Emmeline, and Clorinda, the Irish woman whose opening of a tearoom sets the plot going. The settings are surprising and vivid, and if Tremain doesn’t quite bring them and their story lines together seamlessly, she is still to be applauded for her ambition. This is probably my joint favorite of her novels that I’ve read so far, with The Road Home.
Favorite lines:
We must be unconventional in our joys and find them wherever we can.
life, so often so cruel in the way it thrust the human soul into prisons from which there seemed to be no escape, could sometimes place it athwart an open door.
My rating: 
I read an advanced e-copy via NetGalley.
Between Light and Storm: How We Live with Other Species by Esther Woolfson
 If you’ve read Woolfson’s Corvus, you’ve already met Chicken, an orphaned rook she raised. For over 31 years, Chicken was a constant presence in her home. The recently departed bird is the dedicatee of her new book, feted as “Colleague, companion, friend.” (No mere pet.) Relationships with these creatures with whom she shared her life led her to think differently about how we as humans conceive of the animal world in general. “If I had ever believed humans to be the only ones to live profound and interconnected lives, I couldn’t any more. … If we’re the gods now, shouldn’t we be better than we are?” From her introduction, it’s clear that her sympathy toward the more-than-human world extends even to spiders, and her language throughout – using words like “who” and “his” in reference to animals, rather than “that” or “its” – reinforces the view that all species are equally valuable.
If you’ve read Woolfson’s Corvus, you’ve already met Chicken, an orphaned rook she raised. For over 31 years, Chicken was a constant presence in her home. The recently departed bird is the dedicatee of her new book, feted as “Colleague, companion, friend.” (No mere pet.) Relationships with these creatures with whom she shared her life led her to think differently about how we as humans conceive of the animal world in general. “If I had ever believed humans to be the only ones to live profound and interconnected lives, I couldn’t any more. … If we’re the gods now, shouldn’t we be better than we are?” From her introduction, it’s clear that her sympathy toward the more-than-human world extends even to spiders, and her language throughout – using words like “who” and “his” in reference to animals, rather than “that” or “its” – reinforces the view that all species are equally valuable.
Or, at least, should be. But our attitudes are fundamentally distorted, Woolfson believes, and have been since the days of Aristotle (whose Ladder of Nature is an origin of the ideas that nature is there for man to use) and the Old Testament writers (one of the two creation accounts in Genesis established the idea of “dominion”). From cave paintings to animal sacrifice, intensive farming to fur coats, taxidermy to whaling, she surveys what others have thought and said about how animals are, or should be, perceived. There was more of an academic tone to this book than I expected, and in early chapters I found too much overlap with other works I’ve read about deep time (Time Song, Surfacing, Underland again!).
I most appreciated the fragments of nature writing and memoir and would have liked more in the way of personal reflection. Woolfson’s perspective – as a Jewish woman in Scotland – is quite interesting. She is clearly troubled by how humans exploit animals, but mostly recounts others’ reasoning rather than coming to conclusions of her own. (Though there is a brilliant takedown of the gender politics of Watership Down.) It’s a book that demands more time and attention than I was able to give just now. As I only skimmed it, I’m going to refrain from assigning a rating and will pass this on to my husband and return to it one day. [I do wish the title, on its own (subtitle aside), was more indicative of the contents.]
My thanks to Granta for the free copy for review.
Which of those 600+ September releases can you recommend?
Review: English Animals by Laura Kaye
“Maybe we can see that the animals are like us, or we are like animals.”
Laura Kaye’s impressive debut novel, English Animals, is a fresh take on themes of art, sex, violence and belonging. It has particular resonance in the wake of Brexit, showing the apparent lack of a cohesive English identity in spite of sometimes knee-jerk nationalism.
 The novel takes place within roughly a year and is narrated by Mirka Komárova, a 19-year-old Slovakian who left home suddenly after an argument with her parents and arrives in the English countryside to work for thirty-somethings Richard and Sophie Parker. She doesn’t know what to expect from her new employers: “Richard and Sophie sounded like good names for good people. But they could be anything, they could be completely crazy.”
The novel takes place within roughly a year and is narrated by Mirka Komárova, a 19-year-old Slovakian who left home suddenly after an argument with her parents and arrives in the English countryside to work for thirty-somethings Richard and Sophie Parker. She doesn’t know what to expect from her new employers: “Richard and Sophie sounded like good names for good people. But they could be anything, they could be completely crazy.”
It’s a live-in governess-type arrangement, and yet there are no children – Mirka later learns that Sophie is having trouble getting pregnant. Instead Mirka drives the volatile Parkers to the pub so they can get drunk whenever they want, and also helps with their various money-making ventures: cooking and cleaning for B&B guests and the summer’s wedding parties, serving as a beater for pheasant shoots, and assisting with Richard’s taxidermy business. Her relationship with them remains uncertain: she’s not a servant but not quite an equal either; it’s a careful friendship powered by jokes with Richard and cryptic crossword clues with Sophie.
At first Mirka seems disgusted by Sophie’s shabby family home and the many animals around the place, both living and dead. Initially squeamish about skinning animal corpses, she gets used to it as taxidermy becomes her artistic expression. Taking inspiration from whimsical Victorian portraits of dead animals in costume, she makes intricate modern tableaux with names like Mice Raving, Freelance Squirrels and Rats at the Office Party. When her art catches the eye of a London agent, she starts preparing her pieces for an exhibit and is the subject of a magazine profile. The interviewer writes this about her:
Mirka is someone who understands the philosophical nature of her art. How, in our strange condition of being simultaneously within and outside the animal kingdom, we invest taxidermy with our longing for permanence.
I loved the level of detail about Mirka’s work – it’s rare to encounter such a precise account of handiwork in fiction, as opposed to in nonfiction like Edmund de Waal’s The Hare with Amber Eyes and David Esterly’s The Lost Carving; Kaye herself is a potter, which might explain it – and I appreciated the many meanings that dead animals take on in the novel. They’re by turns food, art objects and sacrificial victims. Taxidermy is a perfect juxtaposition of physicality and the higher echelons of art, a canny way of blending death and beauty.
But of course the human residents of this community also fall into the title’s category: Many of them are what you might call ‘beastly’, and the threat of violence is never far away given Richard and Sophie’s argumentativeness. A promiscuous blonde, Sophie reminded me of Daisy in The Great Gatsby, so often described as careless: “You are a dangerous person, Sophie,” Mirka says. “Don’t say that. I didn’t mean to hurt anything.” Mirka replies, “You don’t care about other things. Everything is a game. Everyone is a toy for you to play with.”
The two different blurbs I’ve seen for the book both give too much away, so I will simply say that there’s an air of sexual tension and latent hostility surrounding this semi-isolated home, and it’s intriguing to watch the dynamic shift between Richard, Sophie and Mirka. I felt that I never quite knew what would happen or how far Kaye would take things.
I did have a few minor misgivings, though: sometimes Mirka’s narration reads like a stilted translation into English, rather than a fluent outpouring; there’s a bit too much domestic detail and heavy-handed symbolism; and the themes of xenophobia and homophobia might have been introduced more subtly, rather than using certain characters as overt mouthpieces.
All the same, I read this with great interest and curiosity throughout. It’s a powerful look at assumptions versus reality, how we approach the Other, and the great effort it takes to change; it’s easier to remain trapped in the roles we’ve acquired. I’d recommend this to readers of Polly Samson, Francesca Segal and even Rachel Johnson (the satire Shire Hell). In particular, I was reminded of Shelter by Jung Yun and Little Children by Tom Perrotta: though suburban in setting, they share Kaye’s preoccupations with sex and violence and the ways we try to hide our true selves beneath a façade of conformity.
This is one of the most striking debut novels I’ve encountered in recent years; it’s left me eager to see what Laura Kaye will do next.
English Animals was published by Little, Brown UK on January 12th. My thanks to Hayley Camis for the review copy.
My rating: 
I was delighted to be asked to participate in the blog tour for English Animals. See below for details of where other reviews and features have appeared or will be appearing soon.


 I picked this up expecting a cute cat tale for children, only realizing afterwards that it’s considered horror. When a grey kitten wanders into their garden, Davy is less enamoured than the rest of the Burrell family. His suspicion mounts as the creature starts holding court in the lounge, expecting lavish meals and attention at all times. His parents and sister seem to be under the cat’s spell in some way, and it’s growing much faster than any young animal should. Davy and his pal George decide to do something about it. Since I’m a cat owner, I’m not big into evil cat stories (e.g., Cat out of Hell by Lynne Truss), and this one was so short as to feel underdeveloped.
I picked this up expecting a cute cat tale for children, only realizing afterwards that it’s considered horror. When a grey kitten wanders into their garden, Davy is less enamoured than the rest of the Burrell family. His suspicion mounts as the creature starts holding court in the lounge, expecting lavish meals and attention at all times. His parents and sister seem to be under the cat’s spell in some way, and it’s growing much faster than any young animal should. Davy and his pal George decide to do something about it. Since I’m a cat owner, I’m not big into evil cat stories (e.g., Cat out of Hell by Lynne Truss), and this one was so short as to feel underdeveloped. 
 “The Old Nurse’s Story” by Elizabeth Gaskell (1852)
“The Old Nurse’s Story” by Elizabeth Gaskell (1852)
 The unnamed narrator is a disgraced teacher who leaves London for a rental cottage on the Hare House estate in Galloway. Her landlord, Grant Henderson, and his rebellious teenage sister, Cass, are still reeling from the untimely death of their brother. The narrator gets caught up in their lives even though her shrewish neighbour warns her not to. There was a lot that I loved about the atmosphere of this one: the southwest Scotland setting; the slow turn of the seasons as the narrator cycles around the narrow lanes and finds it getting dark earlier, and cold; the inclusion of shape-shifting and enchantment myths; the creepy taxidermy up at the manor house; and the peculiar fainting girls/mass hysteria episode that precipitated the narrator’s banishment and complicates her relationship with Cass. The further you get, the more unreliable you realize this narrator is, yet you keep rooting for her. There are a few too many set pieces involving dead animals, and, overall, perhaps more supernatural influences than are fully explored, but I liked Hinchcliffe’s writing enough to look out for what else she will write. (Readalikes:
The unnamed narrator is a disgraced teacher who leaves London for a rental cottage on the Hare House estate in Galloway. Her landlord, Grant Henderson, and his rebellious teenage sister, Cass, are still reeling from the untimely death of their brother. The narrator gets caught up in their lives even though her shrewish neighbour warns her not to. There was a lot that I loved about the atmosphere of this one: the southwest Scotland setting; the slow turn of the seasons as the narrator cycles around the narrow lanes and finds it getting dark earlier, and cold; the inclusion of shape-shifting and enchantment myths; the creepy taxidermy up at the manor house; and the peculiar fainting girls/mass hysteria episode that precipitated the narrator’s banishment and complicates her relationship with Cass. The further you get, the more unreliable you realize this narrator is, yet you keep rooting for her. There are a few too many set pieces involving dead animals, and, overall, perhaps more supernatural influences than are fully explored, but I liked Hinchcliffe’s writing enough to look out for what else she will write. (Readalikes:  Ever since I read
Ever since I read  This nature writing anthology of essays, poems and visual art drew me because of contributor names like GP Gavin Francis (reviewed:
This nature writing anthology of essays, poems and visual art drew me because of contributor names like GP Gavin Francis (reviewed:  After her father’s suicide, Jessa-Lynn Morton takes over the family taxidermy business in central Florida. Despite her excessive drinking and grief over both her father and her best friend and long-time on-and-off girlfriend (also, inconveniently, her brother’s wife) Brynn, who recently took off, she’s just about holding it together. That is, until 1) her mother takes to composing interspecies orgies and S&M scenes in the shop window and 2) her niece and nephew, Lolee and Bastien, start bringing in specimens for taxidermy that they haven’t exactly obtained legally. Gallery owner Lucinda Rex takes an interest in her mother’s ‘art’ and is soon a new romantic interest for Jessa. But the entire family is going to have to face its issues before her professional and love life can be restored.
After her father’s suicide, Jessa-Lynn Morton takes over the family taxidermy business in central Florida. Despite her excessive drinking and grief over both her father and her best friend and long-time on-and-off girlfriend (also, inconveniently, her brother’s wife) Brynn, who recently took off, she’s just about holding it together. That is, until 1) her mother takes to composing interspecies orgies and S&M scenes in the shop window and 2) her niece and nephew, Lolee and Bastien, start bringing in specimens for taxidermy that they haven’t exactly obtained legally. Gallery owner Lucinda Rex takes an interest in her mother’s ‘art’ and is soon a new romantic interest for Jessa. But the entire family is going to have to face its issues before her professional and love life can be restored.
 Mallory is five years into an internship at Swansby House, the London headquarters of Swansby’s dictionary. The dictionary is known for being unfinished – too many of its lexicographers left for WWI and never returned – and for having made-up words. In 1899, Peter Winceworth, the butt of jokes among his colleagues, started composing mountweazels (fake entries) and inserting them into the dictionary. In the contemporary story line, Mallory’s job is to remove the mountweazels as the dictionary is prepared for digitization. But her attention is distracted by anonymous bomb threats and by lingering shame about her sexuality – Mallory thinks she’s “out enough,” but her girlfriend Pip begs to differ.
Mallory is five years into an internship at Swansby House, the London headquarters of Swansby’s dictionary. The dictionary is known for being unfinished – too many of its lexicographers left for WWI and never returned – and for having made-up words. In 1899, Peter Winceworth, the butt of jokes among his colleagues, started composing mountweazels (fake entries) and inserting them into the dictionary. In the contemporary story line, Mallory’s job is to remove the mountweazels as the dictionary is prepared for digitization. But her attention is distracted by anonymous bomb threats and by lingering shame about her sexuality – Mallory thinks she’s “out enough,” but her girlfriend Pip begs to differ. When I worked in a university library and read Middlesex during quiet evenings on the circulation desk in 2009, a colleague asked me, “Is that about the London borough?” My reply: “Er, no, it’s about a hermaphrodite.” That’s an off-putting, clinical sort of word, but it does appear in the first paragraph of this family saga with a difference, after the mythological intensity and medical necessity implied by the killer opening line: “I was born twice: first, as a baby girl, on a remarkably smogless Detroit day in January of 1960; and then again, as a teenage boy, in an emergency room near Petoskey, Michigan, in August of 1974.”
When I worked in a university library and read Middlesex during quiet evenings on the circulation desk in 2009, a colleague asked me, “Is that about the London borough?” My reply: “Er, no, it’s about a hermaphrodite.” That’s an off-putting, clinical sort of word, but it does appear in the first paragraph of this family saga with a difference, after the mythological intensity and medical necessity implied by the killer opening line: “I was born twice: first, as a baby girl, on a remarkably smogless Detroit day in January of 1960; and then again, as a teenage boy, in an emergency room near Petoskey, Michigan, in August of 1974.” I intended to reread Middlesex, which I consider one of my all-time favorite books, but only made it through 60 pages on this occasion. Still, Yamboliev, a Bulgarian-American who teaches at Stanford, reminded me of everything I love about it: the medical theme, the exploration of selfhood, the playful recreation of the past. Drawing parallels with her own family’s move to America, she ponders the disconnection from the home country and the creation of a new life story. “To tell ourselves where we come from—to narrate—is to find a pattern retroactively.” She also looks at literary precursors like Ovid’s Metamorphoses, Herculine Barbin’s memoir, and Balzac’s and Barthes’s writings on a castrato. “Does transformation make the self discontinuous?” is one of her central questions, and she likens Cal’s situation to that of trans men who have to train themselves to speak, dress and act in a convincingly masculine way.
I intended to reread Middlesex, which I consider one of my all-time favorite books, but only made it through 60 pages on this occasion. Still, Yamboliev, a Bulgarian-American who teaches at Stanford, reminded me of everything I love about it: the medical theme, the exploration of selfhood, the playful recreation of the past. Drawing parallels with her own family’s move to America, she ponders the disconnection from the home country and the creation of a new life story. “To tell ourselves where we come from—to narrate—is to find a pattern retroactively.” She also looks at literary precursors like Ovid’s Metamorphoses, Herculine Barbin’s memoir, and Balzac’s and Barthes’s writings on a castrato. “Does transformation make the self discontinuous?” is one of her central questions, and she likens Cal’s situation to that of trans men who have to train themselves to speak, dress and act in a convincingly masculine way.










