Signs of Life: To the Ends of the Earth with a Doctor by Stephen Fabes
Stephen Fabes is an emergency room doctor at St Thomas’s Hospital, London. Not exciting enough for you? Well, he also spent six years of the past decade cycling six continents (so, all bar Antarctica). His statistics are beyond impressive: 53,568 miles, 102 international borders, 1000+ nights of free camping, 26 bicycle tires, and 23 journals filled with his experiences. A warm-up was cycling the length of Chile with his brother at age 19. After medical school in Liverpool and starting his career in London, he found himself restless and again longing for adventure. The round-the-world cycle he planned fell into four sections: London to Cape Town, the West Coast of the Americas, Melbourne to Mumbai, and Hong Kong to home.
Signs of Life is a warm-hearted and laugh-out-loud funny account of Fabes’ travels, achieving a spot-on balance between major world events, the everyday discomforts of long-distance cycling and rough camping, and his humanitarian volunteering. He is a witness to the Occupy movement in Hong Kong, the aftermath of drought and tribal conflict in Africa, and the refugee crisis via the “Jungle” migrant camp in Calais. The desperate situations he saw while putting his medical expertise to good use in short bursts – e.g., at a floating clinic on a Cambodian lake, a malaria research center in Thailand, a leper hospital in Nepal, and a mental health rehabilitation clinic in Mumbai – put into perspective more minor annoyances like fire ants in El Salvador, Indonesian traffic, extreme cold in Mongolia, and camel spiders.

Wherever he went, Fabes met with kindness from strangers, even those who started off seeming hostile – having pitched his tent by a derelict cabin in Peru, he was alarmed to awake to a man pointing a gun at him, but the illicit gold miner soon determined he was harmless and offered him some soup. (Police officers and border guards were perhaps a bit less hospitable.) He also had occasional companions along the route, including a former housemate and a one-time girlfriend. Even limited shared language was enough to form common ground with a stranger-turned-fellow cyclist for a week or so. We get surprising glimpses of how Anglo-American culture permeates the developing world: For some reason, in the ‒Stans everyone’s point of reference when he introduced himself was Steven Seagal.
At nearly 400 pages, the memoir is on the long side, though I can see that it must have felt impossible to condense six years of adventures any further. I was less interested in the potted histories of other famous cyclists’ travels and would have appreciated a clearer sense to the passing of time, perhaps in the form of a date stamp at the head of each chapter. One of my favorite aspects of the book, though, was the use of medical metaphors to link geography to his experiences. Most chapters are titled after health vocabulary; for instance, in “Membranes” he ponders whether country borders are more like scars or cell membranes.
Fabes emphasizes, in a final chapter on the state of the West upon his return in early 2016, that, in all the most important ways, people are the same the world over. Whether in the UK or Southeast Asia, he sees poverty as the major factor in illness, perpetuating the inequality of access to adequate healthcare. Curiosity and empathy are his guides as he approaches each patient’s health as a story. Reflecting on the pandemic, which hit just as he was finalizing the manuscript, he prescribes global cooperation and innovation for this time of uncertainty.
We’re all armchair travelers this year, but this book is especially for you if you enjoy Bill Bryson’s sense of humor, think Dervla Murphy was a badass in Full Tilt, and enjoyed War Doctor by David Nott and/or The Crossway by Guy Stagg. It’s one of my top few predictions for next year’s Wellcome Book Prize – fingers crossed it will go ahead after the 2020 hiatus.
My rating: 
With thanks to Dr Fabes and Profile Books for the free copy for review.
20 Books of Summer, #13–14: Ruth Reichl and Alice Steinbach
Just three weeks remain in this challenge. I’m reading another four books towards it, and have two more to pick up during our mini-break to Devon and Dorset this coming weekend. A few of my choices are long and/or slow-moving reads, though, so I have a feeling I’ll be reading right down to the wire…
Today I have another two memoirs linked by France and its cuisine.
Tender at the Bone: Growing Up at the Table by Ruth Reichl (1998)
 (20 Books of Summer, #13) I’ve read Reichl’s memoirs out of order, starting with Garlic and Sapphires (2005), about her time as a New York Times food critic, and moving on to Comfort Me with Apples (2001), about her involvement in California foodie culture in the 1970s–80s. Whether because I’d been primed by the disclaimer in the author’s note (“I have occasionally embroidered. I learned early that the most important thing in life is a good story”) or not, I sensed that certain characters and scenes were exaggerated here. Although I didn’t enjoy her memoir of her first 30 years as much as either of the other two I’d read, it was still worth reading.
(20 Books of Summer, #13) I’ve read Reichl’s memoirs out of order, starting with Garlic and Sapphires (2005), about her time as a New York Times food critic, and moving on to Comfort Me with Apples (2001), about her involvement in California foodie culture in the 1970s–80s. Whether because I’d been primed by the disclaimer in the author’s note (“I have occasionally embroidered. I learned early that the most important thing in life is a good story”) or not, I sensed that certain characters and scenes were exaggerated here. Although I didn’t enjoy her memoir of her first 30 years as much as either of the other two I’d read, it was still worth reading.
The cover image is a genuine photograph taken by Reichl’s German immigrant father, book designer Ernst Reichl, in 1955. Early on, Reichl had to fend for herself in the kitchen: her bipolar mother hoarded discount food even it was moldy, so the family quickly learned to avoid her dishes made with ingredients that were well past their best. Like Eric Asimov and Anthony Bourdain, whose memoirs I’ve also reviewed this summer, Reichl got turned on to food by a top-notch meal in France. Food was a form of self-expression as well as an emotional crutch in many situations to come: during boarding school in Montreal, her rebellious high school years, and while living off of trendy grains and Dumpster finds at a co-op in Berkeley.
Reichl worked with food in many ways during her twenties. She was a waitress during college in Michigan, and a restaurant collective co-owner in California; she gave cooking lessons; she catered parties; and she finally embarked on a career as a restaurant critic. Her travels took her to France (summer camp counselor; later, wine aficionado), Morocco (with her college roommate), and Crete (a honeymoon visit to her favorite professor). Raised in New York City, she makes her way back there frequently, too. Overall, the book felt a bit scattered to me, with few if any recipes that I would choose to make, and the relationship with a mentally ill mother was so fraught that I will probably avoid Reichl’s two later books focusing on her mother.
Source: Awesomebooks.com
My rating: 
Educating Alice: Adventures of a Curious Woman by Alice Steinbach (2004)
 (20 Books of Summer, #14) Steinbach makes a repeat appearance in my summer reading docket: her 2000 travel book Without Reservations was one of my 2018 selections. In that book, she took a sabbatical during her 50s to explore Paris, England, and Italy. Here she continues her efforts at lifelong learning by taking up some sort of lessons everywhere she goes. The long first section sees her back in Paris, enrolling at the Hotel Ritz’s Escoffier École de Gastronomie Française. She’s self-conscious about having joined late, being older than the other students and having to rely on the translator rather than the chef’s instructions, but she’s determined to keep up as the class makes omelettes, roast quail and desserts.
(20 Books of Summer, #14) Steinbach makes a repeat appearance in my summer reading docket: her 2000 travel book Without Reservations was one of my 2018 selections. In that book, she took a sabbatical during her 50s to explore Paris, England, and Italy. Here she continues her efforts at lifelong learning by taking up some sort of lessons everywhere she goes. The long first section sees her back in Paris, enrolling at the Hotel Ritz’s Escoffier École de Gastronomie Française. She’s self-conscious about having joined late, being older than the other students and having to rely on the translator rather than the chef’s instructions, but she’s determined to keep up as the class makes omelettes, roast quail and desserts.
Full disclosure: I’ve only read the first chapter for now as it’s the only one directly relevant to food – in others she takes dance lessons in Japan, studies art in Cuba, trains Border collies in Scotland, etc. – but I was enjoying it and will go back to it before the end of the year.
Source: Free bookshop
Thinking about the Future with David Farrier & Roman Krznaric (Hay Festival)
My last of three digital Hay Festival* talks this year was by Roman Krznaric, a School of Life philosopher with a background in politics and gardening. I discovered him through Greenbelt Festival eight years ago and have since enjoyed several of his books on the topics of empathy, finding purposeful work, and models for living well. His talk on his upcoming book, The Good Ancestor: How to Think Long Term in a Short Term World, was an ideal follow-up to one of the top three 2020 nonfiction works I’ve read so far:
Footprints: In Search of Future Fossils by David Farrier
Look on my Works, ye Mighty, and despair!
Nothing beside remains. Round the decay
Of that colossal Wreck, boundless and bare
The lone and level sands stretch far away.
~from “Ozymandias” by Percy Bysshe Shelley
In May 2013 a set of fossil human footprints was found at Happisburgh in Norfolk. At 850,000 years old, they were the oldest outside of Africa. In the same month, atmospheric CO2 passed 400 ppm for the first time. It’s via such juxtapositions of past and future, and longevity versus precariousness, that Farrier’s book – a sophisticated lattice of human and planetary history, environmental realism and literary echoes – tells the story of the human impact on the Earth.
Unusually, Farrier is not a historian or a climate scientist, but a senior lecturer in English literature at the University of Edinburgh specializing in nature and place writing, especially in relation to the Anthropocene. That humanities focus allowed him to craft a truly unique, interdisciplinary work in which the canon both foreshadows and responds to environmental collapse. On a sabbatical in Australia, he also gets to hold an ice core taken by an icebreaker, swim above coral reefs and visit a uranium mine exempted from protection in a national park.
 He travels not just through space, but also through time, tracing a plastic bottle from algal bloom to oil to factory to river/landfill to ocean; he thinks about how cultural memory can preserve vanished landscapes; he imagines propitiatory rites arising around radioactive waste to explain poisoned lakes and zinc-lined coffins; and he wonders how to issue appropriate warnings to the future when we don’t even know if English, or language in general, will persist (a nuclear waste storage site in Carlsbad uses a combination of multilingual signs, symbols, monoliths and planned oral tradition, while one in Finland is unmarked).
He travels not just through space, but also through time, tracing a plastic bottle from algal bloom to oil to factory to river/landfill to ocean; he thinks about how cultural memory can preserve vanished landscapes; he imagines propitiatory rites arising around radioactive waste to explain poisoned lakes and zinc-lined coffins; and he wonders how to issue appropriate warnings to the future when we don’t even know if English, or language in general, will persist (a nuclear waste storage site in Carlsbad uses a combination of multilingual signs, symbols, monoliths and planned oral tradition, while one in Finland is unmarked).
Each chapter is an intricate blend of fact, experience and story. For example, “The Insatiable Road” is about cars and the concrete landscapes they zip through – all made possible by oil. Farrier wins a chance to be among the first to cross the new Forth Bridge on foot and finds himself awed by the human achievement. Yet he knows that, in a car, the bridge will be crossed in seconds and soon taken for granted. Whether as a driver or a passenger, we have become detached from the journey and from the places we are travelling through. The road trip, a standard element of twentieth-century art and literature, has lost its lustre. “Really, we have conceded so much,” he writes. “Most of us live and wander only where road networks permit us to, creeping along their edges and lulled into deafness by their constant roar.” Ben Okri’s legend provides the metaphor of a famished road that swallows all in its path.
What will the human species leave behind? “The entire atmosphere now bears the marks of our passage … Perhaps no one will be around to read our traces, but nonetheless we are, everywhere, constantly, and with the most astonishing profligacy, leaving a legacy that will endure for hundreds of thousands or even hundreds of millions of years to come.” That legacy includes the concrete foundations of massive road networks, the remnants of megacities on coastal plains, plastics that will endure for many centuries, carbon and methane locked up in permafrost, the 2300-km fossil of the dead Great Barrier Reef, nuclear waste in isolation plants, jellyfish-dominated oceans and decimated microbial life.
Thinking long term doesn’t come naturally. In the same way that multiple books of 2019 (Time Song, Surfacing, Underland) helped us think about the place of humanity in reference to deep time, Footprints offers an invaluable window onto the deep future. Its dichotomies of hubris and atonement, and culpability versus indifference, are essential to ponder. It was always going to be sobering to read about how we have damaged our only home, but I never found this to be a needlessly depressing book; it is clear-eyed and forthright, but also meditative and beautifully constructed. Life on the planet continues in spite of our alterations, but all the diminishment was unavoidable, and perhaps some of it is remediable still.
My rating: 
 Related reading: Notes from an Apocalypse by Mark O’Connell. I’m only up to page 36 and at the moment it’s just him watching loads of crackpot preppers’ videos on YouTube, but already I think that Footprints should have had this book’s spot on the Wainwright Prize for Writing on Global Conservation longlist (a new prize run in addition to the standard UK nature writing one) for being more directly engaged with conservation issues rather than just humorously commenting on the end-of-the-world mindset.
Related reading: Notes from an Apocalypse by Mark O’Connell. I’m only up to page 36 and at the moment it’s just him watching loads of crackpot preppers’ videos on YouTube, but already I think that Footprints should have had this book’s spot on the Wainwright Prize for Writing on Global Conservation longlist (a new prize run in addition to the standard UK nature writing one) for being more directly engaged with conservation issues rather than just humorously commenting on the end-of-the-world mindset.
Roman Krznaric at Hay Festival
 Krznaric’s discussion of being a “good ancestor” resonated in connection with the long-term thinking of Farrier’s book. “This is the age of the tyranny of the now,” he began, but “humankind has colonized the future” as well, treating it as a tempus nullius where we can dump our ecological waste and tech failures. Yet long-termism is needed more than ever as a way of planning for environmental challenges (and pandemics and the like). Future generations have no say in the decisions we make now that will affect them. To put this in perspective, he showed an image of three spheres, proportionally sized: one represented the 100 billion dead, one was the 7.7 billion currently living, and one was the 6.75 trillion in unborn generations (if the current birth rate continues).
Krznaric’s discussion of being a “good ancestor” resonated in connection with the long-term thinking of Farrier’s book. “This is the age of the tyranny of the now,” he began, but “humankind has colonized the future” as well, treating it as a tempus nullius where we can dump our ecological waste and tech failures. Yet long-termism is needed more than ever as a way of planning for environmental challenges (and pandemics and the like). Future generations have no say in the decisions we make now that will affect them. To put this in perspective, he showed an image of three spheres, proportionally sized: one represented the 100 billion dead, one was the 7.7 billion currently living, and one was the 6.75 trillion in unborn generations (if the current birth rate continues).
It was Jonas Salk, creator of the polio vaccine, who asked, “Are we being good ancestors?” Krznaric invited the audience to come up with examples (in the chat window on the sidebar) of long-term projects through which people are trying to help future generations, such as the Svalbard Seed Depository, the Green New Deal, the 10,000-Year Clock (inside a mountain in the Texas desert), the Long Play piece of music to last 1,000 years, rewilding, archives and libraries, and tree planting. He had also opened the talk with his own modest contribution: he and his partner ‘gave’ their 11-year-old twins their votes in the latest election.
Krznaric elaborated on four of his book’s six ways of thinking about the future: 1) Rethink human nature by using the “acorn brain” (long-term thinking) rather than the “marshmallow brain” (instant gratification). 2) Embark on projects with long time horizons (“cathedral thinking”). 3) Think in terms of legacies, whether familial or transcendent – leaving a gift to the citizens of the future (e.g. The Future Library of 100 books not published or read until 2114). 4) Create a politics for the future, e.g. the citizen assembly movement.
Roman Krznaric at the digital Hay Festival. Q&A led by John Mitchinson (right).
In the case of the UK, Krznaric advocates abolishing the House of Lords, replacing it with a citizens’ assembly and a Minister for the Future, and establishing legal rights for future generations. He noted that globally we’re at a “devil’s fork” where there’s a danger of authoritarian regulations continuing around the world after quarantine ends, endangering the future of social democracy. Instead, we need grassroots activism and “doughnut economics.” He pictures devolution of power away from central governments, with progressive cities becoming new loci of power. Individual actions like vowing not to fly and installing solar panels can inspire peers, but only collective action can tackle environmental breakdown.
 Related reading: I’ll be reviewing Eric Holthaus’s forthcoming book The Future Earth: A Radical Vision for What’s Possible in the Age of Warming for BookBrowse later this month. The meteorologist and science journalist fleshes out some of Krznaric’s ideas, such as a citizen assembly and the cyclical economy, in his proposal for the drastic changes needed over the next three decades.
Related reading: I’ll be reviewing Eric Holthaus’s forthcoming book The Future Earth: A Radical Vision for What’s Possible in the Age of Warming for BookBrowse later this month. The meteorologist and science journalist fleshes out some of Krznaric’s ideas, such as a citizen assembly and the cyclical economy, in his proposal for the drastic changes needed over the next three decades.
*You can access the recorded Hay Festival talks by paying a £10 annual subscription here.
Have you read anything about the deep future?
The Seafarers by Stephen Rutt (Paperback Release)
It’s the paperback release date for The Seafarers: A Journey among Birds by Stephen Rutt, one of my highlights from last year’s summer reading and ultimately one of my top 5 nonfiction reads of 2019.
I’ve been asked to repost my review, and you get a bonus: I’m also posting part of the review my husband wrote for his blog last year, which opens with memories of seabird-rich trips he and I have taken. (Chris is a lecturer in animal ecology at the University of Reading, a Newbury Town councillor, and an off-and-on nature blogger.)
Rebecca’s review:
 In 2016 Rutt left his anxiety-inducing life in London in a search for space and silence. He found plenty of both on the Orkney Islands, where he volunteered at the North Ronaldsay bird observatory for seven months. In the few years that followed, the young naturalist travelled the length and breadth of the British Isles – from Skomer to Shetland – courting encounters with seabirds. He’s surrounded by storm petrels one magical night at Mousa Broch; he runs from menacing skuas; he watches eider and terns and kittiwakes along the northeast coast; he returns to Orkney to marvel at gannets and fulmars. Whether it’s their beauty, majesty, resilience, or associations with freedom, such species are for him a particularly life-enhancing segment of nature to spend time around.
In 2016 Rutt left his anxiety-inducing life in London in a search for space and silence. He found plenty of both on the Orkney Islands, where he volunteered at the North Ronaldsay bird observatory for seven months. In the few years that followed, the young naturalist travelled the length and breadth of the British Isles – from Skomer to Shetland – courting encounters with seabirds. He’s surrounded by storm petrels one magical night at Mousa Broch; he runs from menacing skuas; he watches eider and terns and kittiwakes along the northeast coast; he returns to Orkney to marvel at gannets and fulmars. Whether it’s their beauty, majesty, resilience, or associations with freedom, such species are for him a particularly life-enhancing segment of nature to spend time around.
Discussion of the environmental threats that hit seabirds hardest, such as plastic pollution, make for a timely tie-in to wider conservation issues. Rutt also sees himself as part of a long line of bird-loving travellers, including James Fisher and especially R. M. Lockley, whose stories he weaves in. This is one of the best nature/travel books I’ve read in a long time, especially enjoyable because I’ve been to a lot of the island locations and the elegantly evocative writing, making particularly effective use of varied sentence lengths, brought back to me just what it’s like to be in the far north of Scotland in the midst of an endless summer twilight, a humbled observer as a whole whirlwind of bird life carries on above you.
A favorite passage:
“Gannets nest on the honeycombs of the cliff, in their thousands. They sit in pairs, pointing to the sky, swaying heads. They stir. The scent of the boat’s herring fills the air. They take off, tessellating in a sky that is suddenly as much bird as light. The great skuas lurk.”
Chris’s review
Scotland, 2005. That’s the trip I always cite as my ‘conversion experience’ as a birder. Perhaps the most memorable element was a boat trip out to the seabird colonies of the Treshnish Isles. Puffins were the draw, but other memories are more vivid. The sudden appearance of a great skua, powering through at low level causing consternation among other birds and excitement among birdwatchers. A minke whale blowing spray near the boat. The dark eye of a shag up close, inscrutably ancient, a pterodactyl that somehow survived to the present.

Puffins at Hermaness, Shetland. Photo by Chris Foster.
Captivated by the peace and isolation of Scottish islands and the incredible sights, sounds and smells of seabirds we did it all again the following year, heading farther north. We started on mainland Orkney, travelling overland by train before catching the ferry from Thurso. During a few days on Westray we experienced a small island community, intriguing to a child of English suburbia, though mostly I remember the rain and superb traybakes in the village café. Finally on to Shetland, making our way up to Hermaness, the very northern end of Britain on the island of Unst. Towering skua-ruled cliffs with the most inquisitive, trusting puffins I have ever known, no land between us and the North Pole. Some four years later we visited Skomer in Pembrokeshire, another famed seabird destination, but since then our visits to Britain’s seabird islands have, alas, largely dried up. I’ve caught up with seabirds on and off since but perhaps let the full wonder of seabirds and the magic of islands drift out of my life.

Great skua at Hermaness, Shetland. Photo by Chris Foster.
In that respect The Seafarers was a timely read. It takes the reader, via a series of personal journeys, through the major groups of ocean-going birds that visit Britain while also introducing a significant seabird location in each chapter. It’s an appealing blend of travel, descriptive nature writing, popular science and biography. Author Stephen Rutt balances a highly personal account of what seabirds have meant for him with some solid seabird facts which are well explained, detailed but not at all dense. Rutt is a young birder, naturalist and writer. Since I too am a bearded, balding young (though not nearly so young as he) birder who is not fond of crowds I was probably predisposed to enjoy his voice, and I did, but I also admired its freshness. He successfully avoids the ‘lone white male’ cliché often accused of dominating nature writing. The writing is accomplished throughout and Rutt’s prose is distinctive, concise yet poetic. The life-affirming, simple joy of birding shines through.

Fulmars on Westray, Orkney Islands. Photo by Chris Foster.
The particularly well-crafted short chapter on vagrant birds may be one of those rare pieces of writing to actually change my mind. Where I have lately been inclined toward the view that twitching exotic vagrants is “a morbid act, a premature wake for a waif that won’t last out the day,” as Rutt puts it, I was won over by his “faith in the wondrous, sense-defying, thrilling capacity that birds have of being lost and making that seem … OK.”
The Seafarers follows just two years after Adam Nicolson’s The Seabird’s Cry. The latter is the more complete (and global) treatment of seabirds, what we know about them and why they matter, but that’s not really a criticism of Rutt’s book. The Seafarers is as much an autobiographical account of the transformative power of birding as it is a compilation of seabird lore. What they have in common is that both books are love letters to this extraordinary group of animals.
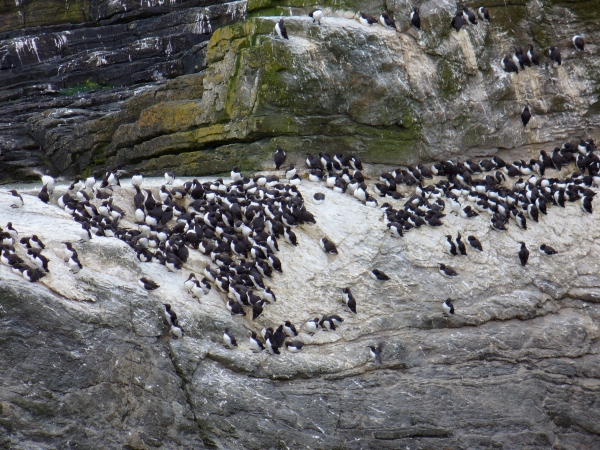

Guillemots at Sumburgh Head, Shetland. Photo by Chris Foster.
Rutt has added his own unique chapter to the shared history of people and seabirds on these islands, as well as establishing himself as a writer with real promise. I look forward to seeing what he turns his thoughts to next.
[The answer was geese; see my review of Rutt’s second 2019 publication, Wintering.]
Note: The Seafarers won the Saltire First Book of the Year award and was longlisted for the Highland Book Prize 2019.
(Order from your local independent bookstore, Hive or Waterstones.)
Reading Ireland Month 2020: Nuala O’Faolain and More
It feels like the whole world has changed in the past week, doesn’t it? I hope you all are keeping well and turning to books for comfort and escape. Reading Ireland Month is run each March by Cathy of 746 Books. I’m wishing you a happy (if subdued) St. Patrick’s Day with this post on the Irish books I’ve been perusing recently. Even before this coronavirus situation heated up, I’d been struggling with my focus, so only one of these was a proper read, while the rest ended up being skims. In the meantime, I’m trying out a new blog design and have been working to create more intuitive menu headings and helpful intro pages.

Are You Somebody? The Accidental Memoir of a Dublin Woman by Nuala O’Faolain (1996)
 Before writing this landmark memoir, O’Faolain was a TV documentary producer and Irish Times columnist. Her upbringing in poverty is reminiscent of Frank McCourt’s: one of nine children, she had a violent father and an alcoholic mother who cheated on each other and never seemed to achieve happiness. Educated at a convent school and at university in Dublin (until she dropped out), she was a literary-minded romantic who bounced between relationships and couldn’t decide whether marriage or a career should be her highest aim. Though desperate not to become her mother – a bitter, harried woman who’d wanted to be a book reviewer – she didn’t want to miss out on a chance for love either.
Before writing this landmark memoir, O’Faolain was a TV documentary producer and Irish Times columnist. Her upbringing in poverty is reminiscent of Frank McCourt’s: one of nine children, she had a violent father and an alcoholic mother who cheated on each other and never seemed to achieve happiness. Educated at a convent school and at university in Dublin (until she dropped out), she was a literary-minded romantic who bounced between relationships and couldn’t decide whether marriage or a career should be her highest aim. Though desperate not to become her mother – a bitter, harried woman who’d wanted to be a book reviewer – she didn’t want to miss out on a chance for love either.
O’Faolain feels she was born slightly too early to benefit from the women’s movement. “I could see sexism in operation everywhere in society; once your consciousness goes ping you can never again stop seeing that. But I was quite unaware of how consistently I put the responsibility for my personal happiness off onto men.” Chapter 16 is a standout, though with no explanation (all her other lovers were men) it launches into an account of her 15 years living with Nell McCafferty, “by far the most life-giving relationship of my life.”
Although this is in many respects an ordinary story, the geniality and honesty of the writing account for its success. It was an instant bestseller in Ireland, spending 20 weeks at number one, and made the author a household name. I especially loved her encounters with literary figures. For instance, on a year’s scholarship at Hull she didn’t quite meet Philip Larkin, who’d been tasked with looking after her, but years later had a bizarre dinner with him and his mother, both rather deaf; and David Lodge was a friend. The boarding school section reminded me of The Country Girls. Two bookish memoirs I’d recommend as readalikes are Ordinary Dogs by Eileen Battersby and Leave Me Alone, I’m Reading by Maureen Corrigan. 
Skims (all:  )
)
Actress by Anne Enright (2020)
 The Green Road is among my most memorable reads of the past five years, so I was eagerly awaiting Enright’s new novel, which is on the Women’s Prize longlist. I read the first 30 pages and found I wasn’t warming to the voice or main characters. Norah is a novelist who, prompted by an interviewer, realizes the story she most needs to tell is her mother’s. Katherine O’Dell was “a great fake,” an actress who came to epitomize Irishness even though she was actually English. Her slow-burning backstory is punctuated by trauma and mental illness. “She was a great piece of anguish, madness and sorrow,” Norah concludes. I could easily see this making the Women’s Prize shortlist and earning a Booker nomination as well. It’s the sort of book I’ll need to come back to some years down the line to fully appreciate.
The Green Road is among my most memorable reads of the past five years, so I was eagerly awaiting Enright’s new novel, which is on the Women’s Prize longlist. I read the first 30 pages and found I wasn’t warming to the voice or main characters. Norah is a novelist who, prompted by an interviewer, realizes the story she most needs to tell is her mother’s. Katherine O’Dell was “a great fake,” an actress who came to epitomize Irishness even though she was actually English. Her slow-burning backstory is punctuated by trauma and mental illness. “She was a great piece of anguish, madness and sorrow,” Norah concludes. I could easily see this making the Women’s Prize shortlist and earning a Booker nomination as well. It’s the sort of book I’ll need to come back to some years down the line to fully appreciate.
Cal by Bernard MacLaverty (1983)
 As Catholics, Cal McCluskey and his father are a rarity in their community and fear attacks on their home. Resistant to join his father in working at the local abattoir, Cal spends his days doing odd jobs and lurking around the public library – he has a crush on a married librarian named Marcella. Aimless and impressionable, he’s easily talked into acting as a driver for Crilly and Skeffington, the kind of associates who have gotten him branded as “Fenian scum.” The novella reflects on the futility of cycles of violence (“If you’re not part of the solution, you’re part of the problem,” Crilly says, to which Cal replies, “But it all seems so pointless”), but is definitely a period piece. Cal is not the most sympathetic of protagonists. I didn’t enjoy this as much as the two other books I’ve read by MacLaverty.
As Catholics, Cal McCluskey and his father are a rarity in their community and fear attacks on their home. Resistant to join his father in working at the local abattoir, Cal spends his days doing odd jobs and lurking around the public library – he has a crush on a married librarian named Marcella. Aimless and impressionable, he’s easily talked into acting as a driver for Crilly and Skeffington, the kind of associates who have gotten him branded as “Fenian scum.” The novella reflects on the futility of cycles of violence (“If you’re not part of the solution, you’re part of the problem,” Crilly says, to which Cal replies, “But it all seems so pointless”), but is definitely a period piece. Cal is not the most sympathetic of protagonists. I didn’t enjoy this as much as the two other books I’ve read by MacLaverty.
Full Tilt: Ireland to India with a Bicycle by Dervla Murphy (1965)
 Murphy and her bike “Roz” set out on an epic Fermor-like journey in the first six months of 1963. She covered 60 to 100 miles a day, facing sunburn, punctured tires and broken ribs. She was relieved she brought a gun: it came in handy for fending off wolves, deterring a would-be rapist, and preventing bike thieves. For some reason travel books are slow, painstaking reads for me. I never got into the flow of this one, and was troubled by snap judgments about groups of people – “I know instinctively the temper of a place, after being five minutes with the inhabitants. … the Afghans are, on balance, much dirtier in clothes, personal habits and dwellings than either the Turks or Persians.” Murphy does have a witty turn of phrase, though, e.g. “I suppose I’ll get used to it but at the moment I wouldn’t actually say that camel’s milk is my favourite beverage.”
Murphy and her bike “Roz” set out on an epic Fermor-like journey in the first six months of 1963. She covered 60 to 100 miles a day, facing sunburn, punctured tires and broken ribs. She was relieved she brought a gun: it came in handy for fending off wolves, deterring a would-be rapist, and preventing bike thieves. For some reason travel books are slow, painstaking reads for me. I never got into the flow of this one, and was troubled by snap judgments about groups of people – “I know instinctively the temper of a place, after being five minutes with the inhabitants. … the Afghans are, on balance, much dirtier in clothes, personal habits and dwellings than either the Turks or Persians.” Murphy does have a witty turn of phrase, though, e.g. “I suppose I’ll get used to it but at the moment I wouldn’t actually say that camel’s milk is my favourite beverage.”
My Father’s Wake: How the Irish Teach Us to Live, Love and Die by Kevin Toolis (2017)
 Toolis is a journalist and filmmaker from Dookinella, on an island off the coast of County Mayo. His father Sonny’s pancreatic cancer prompted him to return to the ancestral village and reflect on his own encounters with death. As a young man he had tuberculosis and stayed on a male chest ward with longtime smokers; despite a bone marrow donation, his older brother Bernard died from leukemia.
Toolis is a journalist and filmmaker from Dookinella, on an island off the coast of County Mayo. His father Sonny’s pancreatic cancer prompted him to return to the ancestral village and reflect on his own encounters with death. As a young man he had tuberculosis and stayed on a male chest ward with longtime smokers; despite a bone marrow donation, his older brother Bernard died from leukemia.
As a reporter during the Troubles and in Malawi and Gaza, Toolis often witnessed death, but at home in rural Ireland he saw a model for how it should be: accepted, and faced with the support of a whole community. People made a point of coming to see Sonny as he was dying. Keeping the body in the home and holding a wake are precious opportunities to be with the dead. Death is what’s coming for us all, so why not make its acquaintance? Toolis argues.
I’ve read so much around the topic that books like this don’t stand out anymore, and while I preferred the general talk of death to the family memoir bits, it also made very familiar points. At any rate, his description of his mother’s death is just how I want to go: “She quietly died of a heart attack with a cup of tea and a biscuit on a sunny May morning.”
 Adichie filters an epic account of Nigeria’s civil war through the experience of twin sisters, Olanna and Kainene, and those closest to them. The wealthy chief’s daughters from Lagos drift apart: Olanna goes to live with Odenigbo, a math professor; Kainene is a canny businesswoman with a white lover, Richard Churchill, who is fascinated by Igbo art and plans to write a book about his experiences in Africa. Gradually, though, he realizes that the story of Biafra is not his to tell.
Adichie filters an epic account of Nigeria’s civil war through the experience of twin sisters, Olanna and Kainene, and those closest to them. The wealthy chief’s daughters from Lagos drift apart: Olanna goes to live with Odenigbo, a math professor; Kainene is a canny businesswoman with a white lover, Richard Churchill, who is fascinated by Igbo art and plans to write a book about his experiences in Africa. Gradually, though, he realizes that the story of Biafra is not his to tell. Kapuściński was a foreign correspondent in Africa for 40 years and lent his name to an international prize for literary reportage. This book of essays spans several decades and lots of countries, yet feels like a cohesive narrative. The author sees many places right on the cusp of independence or in the midst of coup d’états – including Nigeria, a nice tie-in to the Adichie. Living among the people rather than removed in some white enclave, he develops a voice that is surprisingly undated and non-colonialist. While his presence as the observer is undeniable – especially when he falls ill with malaria and then tuberculosis – he lets the situation on the ground take precedence over the memoir aspect. I’m only halfway through, but I fully expect this to stand out as one of the best travel books I’ve ever read.
Kapuściński was a foreign correspondent in Africa for 40 years and lent his name to an international prize for literary reportage. This book of essays spans several decades and lots of countries, yet feels like a cohesive narrative. The author sees many places right on the cusp of independence or in the midst of coup d’états – including Nigeria, a nice tie-in to the Adichie. Living among the people rather than removed in some white enclave, he develops a voice that is surprisingly undated and non-colonialist. While his presence as the observer is undeniable – especially when he falls ill with malaria and then tuberculosis – he lets the situation on the ground take precedence over the memoir aspect. I’m only halfway through, but I fully expect this to stand out as one of the best travel books I’ve ever read. Berne, something of a one-hit wonder, is not among the more respected Women’s Prize alumni – look at the writers she was up against in the shortlist and you have to marvel that she was considered worthier than Barbara Kingsolver (The Poisonwood Bible) and Toni Morrison (Paradise). However, I enjoyed this punchy tale. Marsha remembers the summer of 1972, when her father left her mother for Aunt Ada and news came of a young boy’s sexual assault and murder in the woods behind a mall. “If you hadn’t known what had happened in our neighborhood, the street would have looked like any other suburban street in America.”
Berne, something of a one-hit wonder, is not among the more respected Women’s Prize alumni – look at the writers she was up against in the shortlist and you have to marvel that she was considered worthier than Barbara Kingsolver (The Poisonwood Bible) and Toni Morrison (Paradise). However, I enjoyed this punchy tale. Marsha remembers the summer of 1972, when her father left her mother for Aunt Ada and news came of a young boy’s sexual assault and murder in the woods behind a mall. “If you hadn’t known what had happened in our neighborhood, the street would have looked like any other suburban street in America.” Just as the Berne is a coming-of-age story masquerading as a mystery, from the title and cover this looked like it would be chick lit, but – though it has an overall breezy tone – it’s actually pretty chewy New York City literary fiction that should please fans of
Just as the Berne is a coming-of-age story masquerading as a mystery, from the title and cover this looked like it would be chick lit, but – though it has an overall breezy tone – it’s actually pretty chewy New York City literary fiction that should please fans of  Sarah Bennett, who went straight from university in Oxford to Paris for want of a better idea of what to do with her life, is called home to Warwickshire to be a bridesmaid in the wedding of her older sister, Louise, to Stephen Halifax, a wealthy novelist. Afterwards, Sarah decides to move to London and share a flat with a friend whose marriage has recently ended. As the months pass, she figures out life as a single girl in a big city and attends parties hosted by Louise – back from an extended European honeymoon – and others. Sarah eventually works out, from gossip and from confronting Louise herself, that her sister’s marriage isn’t as idyllic as it appeared. Both sisters find themselves at a loss as for what to do next.
Sarah Bennett, who went straight from university in Oxford to Paris for want of a better idea of what to do with her life, is called home to Warwickshire to be a bridesmaid in the wedding of her older sister, Louise, to Stephen Halifax, a wealthy novelist. Afterwards, Sarah decides to move to London and share a flat with a friend whose marriage has recently ended. As the months pass, she figures out life as a single girl in a big city and attends parties hosted by Louise – back from an extended European honeymoon – and others. Sarah eventually works out, from gossip and from confronting Louise herself, that her sister’s marriage isn’t as idyllic as it appeared. Both sisters find themselves at a loss as for what to do next.
 Another sisters novel, and the first book in my
Another sisters novel, and the first book in my 
 In 2009, Barkham set out to revive the childhood butterfly-watching hobby he’d shared with his father. The UK is home to 59 species, a manageable number to attempt to see in a season, although it does require a fair bit of travel and insider knowledge. I’ve read too much general history about the human relationship with butterflies (via Rainbow Dust by Peter Marren, which came out a few years later, and
In 2009, Barkham set out to revive the childhood butterfly-watching hobby he’d shared with his father. The UK is home to 59 species, a manageable number to attempt to see in a season, although it does require a fair bit of travel and insider knowledge. I’ve read too much general history about the human relationship with butterflies (via Rainbow Dust by Peter Marren, which came out a few years later, and 
 Dark, Salt, Clear: Life in a Cornish Fishing Town by Lamorna Ash: In her early 20s, Ash made multiple trips from London to stay in Newlyn: walking to the cove that bears her name, going out on fishing trawlers, and getting accepted into the small community. Gruelling and lonely, the fishermen’s way of life is fading away. The book goes deeper into Cornish history than non-locals need, but I enjoyed the literary allusions – the title is from Elizabeth Bishop. I liked the writing, but this was requested after me at the library, so I could only skim it.
Dark, Salt, Clear: Life in a Cornish Fishing Town by Lamorna Ash: In her early 20s, Ash made multiple trips from London to stay in Newlyn: walking to the cove that bears her name, going out on fishing trawlers, and getting accepted into the small community. Gruelling and lonely, the fishermen’s way of life is fading away. The book goes deeper into Cornish history than non-locals need, but I enjoyed the literary allusions – the title is from Elizabeth Bishop. I liked the writing, but this was requested after me at the library, so I could only skim it. 
 Bird Therapy by Joe Harkness: In 2013, Harkness was in such a bad place that he attempted suicide. Although he’s continued to struggle with OCD and depression in the years since then, birdwatching has given him a new lease on life. Avoiding the hobby’s more obsessive, competitive aspects (like listing and twitching), he focuses on the benefits of outdoor exercise and mindfulness. He can be lyrical when describing his Norfolk patch and some of his most magical sightings, but the writing is weak. (My husband helped crowdfund the book via Unbound.)
Bird Therapy by Joe Harkness: In 2013, Harkness was in such a bad place that he attempted suicide. Although he’s continued to struggle with OCD and depression in the years since then, birdwatching has given him a new lease on life. Avoiding the hobby’s more obsessive, competitive aspects (like listing and twitching), he focuses on the benefits of outdoor exercise and mindfulness. He can be lyrical when describing his Norfolk patch and some of his most magical sightings, but the writing is weak. (My husband helped crowdfund the book via Unbound.) 
 Dancing with Bees: A Journey Back to Nature by Brigit Strawbridge Howard: Bees were the author’s gateway into a general appreciation of nature, something she lost for a time in midlife because of the rat race and family complications. Allotment gardening gives her opportunities to observe bee behaviour and marvel at their various lookalikes (like hoverflies), identify plants, work on herbal remedies, and photograph her finds. She delights in discovery and is devoted to lifelong learning in a book characterized by curiosity and warmth. (On my runners-up of 2019 list)
Dancing with Bees: A Journey Back to Nature by Brigit Strawbridge Howard: Bees were the author’s gateway into a general appreciation of nature, something she lost for a time in midlife because of the rat race and family complications. Allotment gardening gives her opportunities to observe bee behaviour and marvel at their various lookalikes (like hoverflies), identify plants, work on herbal remedies, and photograph her finds. She delights in discovery and is devoted to lifelong learning in a book characterized by curiosity and warmth. (On my runners-up of 2019 list) 




 I think this year’s is an especially appealing longlist. It’s great to see small presses and debut authors getting recognition. I’ve now read 8 out of 13 (and skimmed one), and am interested in the rest, too, especially The Frayed Atlantic Edge by David Gange. The final three, all combining nature and (auto)biographical writing, are On the Red Hill by Mike Parker, The Well-Gardened Mind by Sue Stuart-Smith, and Rootbound: Rewilding a Life by Alice Vincent.
I think this year’s is an especially appealing longlist. It’s great to see small presses and debut authors getting recognition. I’ve now read 8 out of 13 (and skimmed one), and am interested in the rest, too, especially The Frayed Atlantic Edge by David Gange. The final three, all combining nature and (auto)biographical writing, are On the Red Hill by Mike Parker, The Well-Gardened Mind by Sue Stuart-Smith, and Rootbound: Rewilding a Life by Alice Vincent.




 Barron is best known for her Jane Austen Mysteries series. Here she takes up the relationship between Virginia Woolf and Vita Sackville-West and crafts a conspiracy theory / alternative history in which Virginia did not commit suicide upon her disappearance in March 1941 but hid with Vita at Sissinghurst, her Kent home with the famous gardens. Investigating this in the autumn of 2008 are Jo Bellamy, an American garden designer who has been tasked with recreating Sackville-West’s famous White Garden at her wealthy client’s upstate New York estate, and Peter Llewelyn, a Sotheby’s employee who helps Jo authenticate a journal she finds hidden in a gardener’s shed at Sissinghurst.
Barron is best known for her Jane Austen Mysteries series. Here she takes up the relationship between Virginia Woolf and Vita Sackville-West and crafts a conspiracy theory / alternative history in which Virginia did not commit suicide upon her disappearance in March 1941 but hid with Vita at Sissinghurst, her Kent home with the famous gardens. Investigating this in the autumn of 2008 are Jo Bellamy, an American garden designer who has been tasked with recreating Sackville-West’s famous White Garden at her wealthy client’s upstate New York estate, and Peter Llewelyn, a Sotheby’s employee who helps Jo authenticate a journal she finds hidden in a gardener’s shed at Sissinghurst.

 This is my favorite of the six books I’ve now read by Hill. Early one spring, Ruth Bryce’s husband, Ben, dies in a forestry accident. They had been only married a year and now here she is, aged 20 and a widow. Ben’s little brother, 14-year-old Jo, is a faithful visitor, but after the funeral many simply leave Ruth alone. Ben’s death is a “stone cast into still water,” whose ripples spread out beyond his immediate family.
This is my favorite of the six books I’ve now read by Hill. Early one spring, Ruth Bryce’s husband, Ben, dies in a forestry accident. They had been only married a year and now here she is, aged 20 and a widow. Ben’s little brother, 14-year-old Jo, is a faithful visitor, but after the funeral many simply leave Ruth alone. Ben’s death is a “stone cast into still water,” whose ripples spread out beyond his immediate family.
 This serves as a prelude to the eight journals for which Sarton would become famous. It’s a low-key memoir about setting up home in the tiny town of Nelson, New Hampshire, making a garden and meeting the salt-of-the-earth locals who provided her support system and are immortalized in fictional form in the novel she published two years later,
This serves as a prelude to the eight journals for which Sarton would become famous. It’s a low-key memoir about setting up home in the tiny town of Nelson, New Hampshire, making a garden and meeting the salt-of-the-earth locals who provided her support system and are immortalized in fictional form in the novel she published two years later,  Philip Rhayader is a lonely bird artist on the Essex marshes by an abandoned lighthouse. “His body was warped, but his heart was filled with love for wild and hunted things. He was ugly to look upon, but he created great beauty.” One day a little girl, Fritha, brings him an injured snow goose and he puts a splint on its wing. The recovered bird becomes a friend to them both, coming back each year to spend time at Philip’s makeshift bird sanctuary. As Fritha grows into a young woman, she and Philip fall in love (slightly creepy), only for him to leave to help with the evacuation of Dunkirk. This is a melancholy and in some ways predictable little story. It was originally published in the Saturday Evening Post in 1940 and became a book the following year. I read a lovely version illustrated by Angela Barrett. It’s the second of Gallico’s animal fables I’ve read; I slightly preferred
Philip Rhayader is a lonely bird artist on the Essex marshes by an abandoned lighthouse. “His body was warped, but his heart was filled with love for wild and hunted things. He was ugly to look upon, but he created great beauty.” One day a little girl, Fritha, brings him an injured snow goose and he puts a splint on its wing. The recovered bird becomes a friend to them both, coming back each year to spend time at Philip’s makeshift bird sanctuary. As Fritha grows into a young woman, she and Philip fall in love (slightly creepy), only for him to leave to help with the evacuation of Dunkirk. This is a melancholy and in some ways predictable little story. It was originally published in the Saturday Evening Post in 1940 and became a book the following year. I read a lovely version illustrated by Angela Barrett. It’s the second of Gallico’s animal fables I’ve read; I slightly preferred 

 “A Search for the World’s Purest, Deepest Snowfall” reads the subtitle on the cover. English set out from his home in London for two years of off-and-on travel in snowy places, everywhere from Greenland to Washington State. In Jericho, Vermont, he learns about Wilson Bentley, an amateur scientist who was the first to document snowflake shapes through microscope photographs. In upstate New York, he’s nearly stranded during the Blizzard of 2006. He goes skiing in France and learns about the deadliest avalanches – Britain’s worst was in Lewes in 1836. In Scotland’s Cairngorms, he learns how those who work in the ski industry are preparing for the 60–80% reduction of snow predicted for this century. An appendix dubbed “A Snow Handbook” gives some technical information on how snow forms, what the different crystal shapes are called, and how to build an igloo, along with whimsical lists of 10 snow stories (I’ve read six), 10 snowy films, etc.
“A Search for the World’s Purest, Deepest Snowfall” reads the subtitle on the cover. English set out from his home in London for two years of off-and-on travel in snowy places, everywhere from Greenland to Washington State. In Jericho, Vermont, he learns about Wilson Bentley, an amateur scientist who was the first to document snowflake shapes through microscope photographs. In upstate New York, he’s nearly stranded during the Blizzard of 2006. He goes skiing in France and learns about the deadliest avalanches – Britain’s worst was in Lewes in 1836. In Scotland’s Cairngorms, he learns how those who work in the ski industry are preparing for the 60–80% reduction of snow predicted for this century. An appendix dubbed “A Snow Handbook” gives some technical information on how snow forms, what the different crystal shapes are called, and how to build an igloo, along with whimsical lists of 10 snow stories (I’ve read six), 10 snowy films, etc.
 This has a very similar format and scope to The Snow Tourist, with Campbell ranging from Greenland and continental Europe to the USA in her search for the science and stories of ice. For English’s chapter on skiing, substitute a section on ice skating. I only skimmed this one because – in what I’m going to put down to a case of reader–writer mismatch – I started it three times between November 2018 and now and could never get further than page 60. See these reviews from
This has a very similar format and scope to The Snow Tourist, with Campbell ranging from Greenland and continental Europe to the USA in her search for the science and stories of ice. For English’s chapter on skiing, substitute a section on ice skating. I only skimmed this one because – in what I’m going to put down to a case of reader–writer mismatch – I started it three times between November 2018 and now and could never get further than page 60. See these reviews from  The travails of his long trial runs with the dogs – the sled flipping over, having to walk miles after losing control of the dogs, being sprayed in the face by multiple skunks – sound bad enough, but once the Iditarod begins the misery ramps up. The course is nearly 1200 miles, over 17 days. It’s impossible to stay warm or get enough food, and a lack of sleep leads to hallucinations. At one point he nearly goes through thin ice. At another he’s run down by a moose. He also watches in horror as a fellow contestant kicks a dog to death.
The travails of his long trial runs with the dogs – the sled flipping over, having to walk miles after losing control of the dogs, being sprayed in the face by multiple skunks – sound bad enough, but once the Iditarod begins the misery ramps up. The course is nearly 1200 miles, over 17 days. It’s impossible to stay warm or get enough food, and a lack of sleep leads to hallucinations. At one point he nearly goes through thin ice. At another he’s run down by a moose. He also watches in horror as a fellow contestant kicks a dog to death. Two nonfiction books entitled Wintering:
Two nonfiction books entitled Wintering: